
Audio downsampling is the most popular method of changing the sampling rate. This is easily explained, because this is the easiest way to reduce the size of an audio file. In the previous article, we already found out that upsampling does not improve quality, so studio recordings are always made in high-resolution formats, and later converted to the most common CD and DVD formats.
The most important thing you need to remember is that downsampling irreversibly reduces the quality of the audio track. In the best case, some of the samples are simply discarded, and with non-integer divisors, the remaining samples can be changed by interpolation. Therefore, always keep an original copy when processing.
1 Why is downsampling needed?
The main audio standards are still CD (44100 Hz) and DVD (48000 Hz). Master recordings have been using 96 kHz and even 192 kHz for a while now. So, whether you like it or not, any audio disc you buy has already been created using downsampling.
Yes, you can now download high-definition audio, which is great for a home hi-fi system. But when it comes to mobile devices, it's still important to keep the audio file sizes down. At some point, you'll probably want to create a separate copy of the album for your smartphone, which usually has a 48 kHz DAC. Just a heads-up: most built-in sound cards have a limitation, too.
When you're listening to high-resolution audio on a computer, you're actually using the Windows audio subsystem, which takes all the sounds you're hearing and puts them into a system format that's chosen in the control panel. You can avoid this by choosing the right settings or using sound players with bit-perfect mode.
Another popular reason for audio downsampling these days is Machine Learning. Almost all neural networks require audio at the same sampling rate with which they were trained. One of the important areas of AI is improving the quality of speech recordings, and all of them usually have a low sampling rate. There is no way to do this without downsampling, because the result is worth it.
If you're downsampling audio, it's important to focus on the frequency range of the original source. The Nyquist-Shannon theorem says that the sampling rate should be twice the highest audio frequency. You can safely apply the strongest reduction to speech recordings because the frequency range of the human voice doesn't exceed 4000 Hz.
2 How to downsample audio
We have already considered one of the resampling options in batch mode using an audio converter. Now let's look at another, no less common, way to change the sampling rate using an audio editor.
If you haven't already, just download the editor from the link above and install it on your computer. It's pretty straightforward.
- Open the audio file however you like and make all the necessary changes to the audio.
- Next, open the "Operations" menu and select "Convert audio...".
- In the new window that opens, choose a new sampling frequency and click OK.
- Go ahead and save the file.
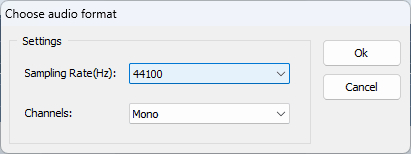
You might be surprised when you try to save the file and it doesn't give you the original format. It could be that it doesn't support the new sampling rate, for example.
What's the benefit of this method compared to downsampling in a converter or any other command line utility? The great thing is that you can see the result for yourself. If there are any issues with resampling, you'll see sharp peaks or a straight line where there should be normal samples.
3 Useful tips
- Always use downsampling at the final stage of processing. Any audio processing is best done at the maximum sampling rate.
- If the number of channels decreases, first do a downmix, and then downsampling, since this is a more resource-intensive operation.
- Don't trust downsampling to codecs. For example, lame mp3 encoder uses an internal resampler that uses a simplified algorithm. It is not able to compete with resamplers used in audio editors.
- When using lossy compression, the sample rate does not affect the file size. This only works for codecs with lossless compression.
4 Conclusion
I'd say the second option of changing the sampling frequency is much more popular. One advantage of reducing the audio file size is that it makes it easier to send files by email. However, they shouldn't get too caught up in the poor sound quality. With the right tools and know-how, audio downsampling is a breeze. If you follow the steps in this guide, you can downsample your audio files effectively and avoid making the same mistakes others have made.
